<!-- .github/pull_request_template.md --> ## Description <!-- Provide a clear description of the changes in this PR --> - Added _filter_instances to BaseBenchmarkAdapter supporting filtering by IDs, indices, or JSON files. - Updated HotpotQAAdapter and MusiqueQAAdapter to use the base class filtering. - Added instance_filter parameter to corpus builder pipeline. - Extracted _get_raw_corpus method in both adapters for better code organization ## DCO Affirmation I affirm that all code in every commit of this pull request conforms to the terms of the Topoteretes Developer Certificate of Origin <!-- This is an auto-generated comment: release notes by coderabbit.ai --> ## Summary by CodeRabbit - **New Features** - Corpus loading and building now support a flexible filtering option, allowing users to apply custom criteria to tailor the retrieved data. - **Refactor** - The extraction process has been reorganized to separately handle text content and associated metadata, enhancing clarity and overall workflow efficiency. <!-- end of auto-generated comment: release notes by coderabbit.ai --> |
||
|---|---|---|
| .data | ||
| .dlt | ||
| .github | ||
| alembic | ||
| assets | ||
| bin | ||
| cognee | ||
| cognee-frontend | ||
| cognee-mcp | ||
| evals | ||
| examples | ||
| helm | ||
| licenses | ||
| notebooks | ||
| profiling | ||
| tests | ||
| tools | ||
| .dockerignore | ||
| .env.template | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| .pre-commit-config.yaml | ||
| .pylintrc | ||
| .python-version | ||
| alembic.ini | ||
| CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md | ||
| cognee-gui.py | ||
| CONTRIBUTING.md | ||
| DCO.md | ||
| docker-compose.yml | ||
| Dockerfile | ||
| Dockerfile_modal | ||
| entrypoint.sh | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| modal_deployment.py | ||
| mypy.ini | ||
| NOTICE.md | ||
| poetry.lock | ||
| pyproject.toml | ||
| README.md | ||

cognee - memory layer for AI apps and Agents
Demo . Learn more · Join Discord
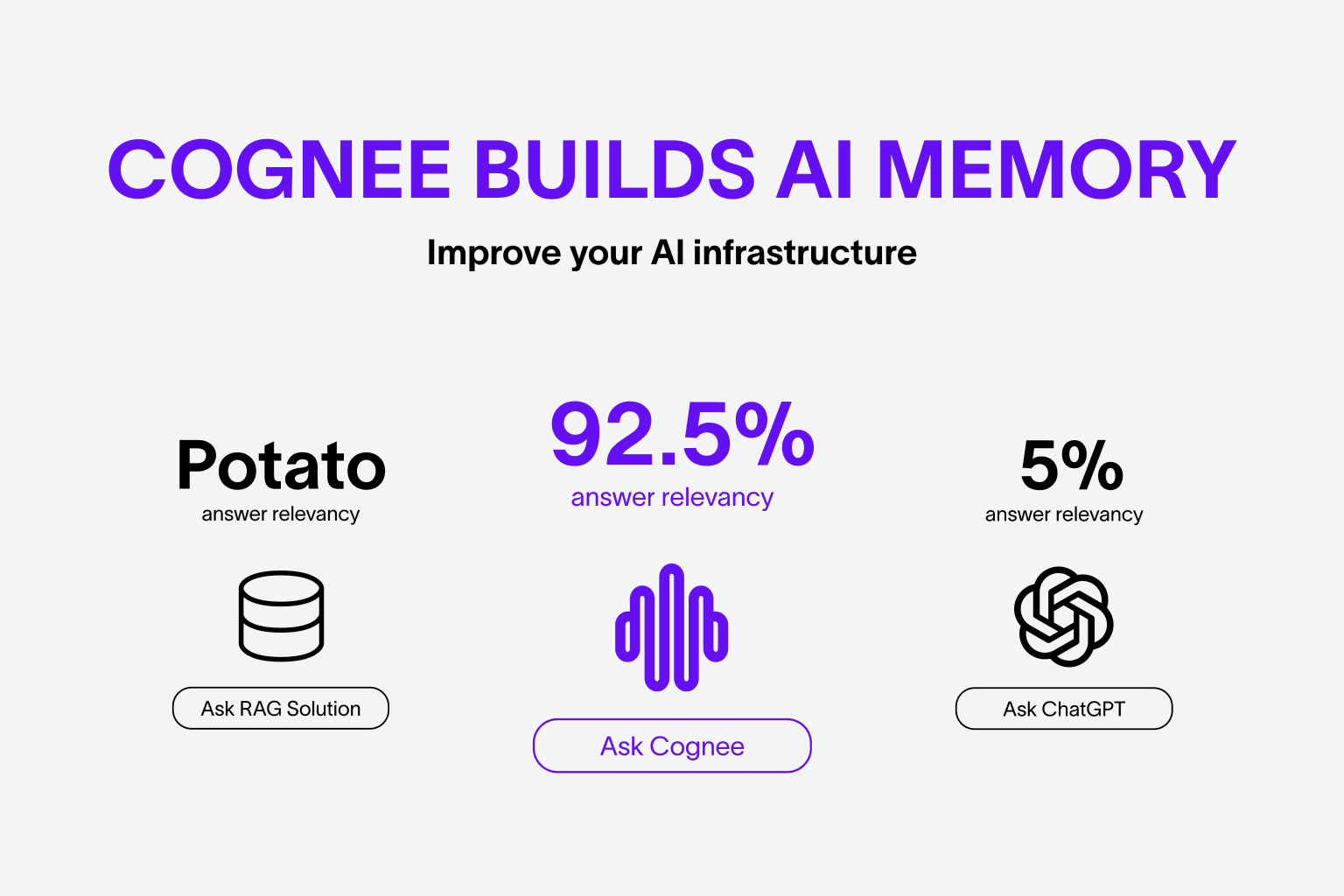
AI Agent responses you can rely on.
Build dynamic Agent memory using scalable, modular ECL (Extract, Cognify, Load) pipelines.
More on use-cases.
Features
- Interconnect and retrieve your past conversations, documents, images and audio transcriptions
- Reduce hallucinations, developer effort, and cost.
- Load data to graph and vector databases using only Pydantic
- Manipulate your data while ingesting from 30+ data sources
Get Started
Get started quickly with a Google Colab notebook or starter repo
Contributing
Your contributions are at the core of making this a true open source project. Any contributions you make are greatly appreciated. See CONTRIBUTING.md for more information.
📦 Installation
You can install Cognee using either pip, poetry, uv or any other python package manager.
With pip
pip install cognee
💻 Basic Usage
Setup
import os
os.environ["LLM_API_KEY"] = "YOUR OPENAI_API_KEY"
You can also set the variables by creating .env file, using our template. To use different LLM providers, for more info check out our documentation
Simple example
Add LLM_API_KEY to .env using the command bellow.
echo "LLM_API_KEY=YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY" > .env
You can see available env variables in the repository .env.template file. If you don't specify it otherwise, like in this example, SQLite (relational database), LanceDB (vector database) and NetworkX (graph store) will be used as default components.
This script will run the default pipeline:
import cognee
import asyncio
from cognee.modules.search.types import SearchType
async def main():
# Create a clean slate for cognee -- reset data and system state
await cognee.prune.prune_data()
await cognee.prune.prune_system(metadata=True)
# cognee knowledge graph will be created based on this text
text = """
Natural language processing (NLP) is an interdisciplinary
subfield of computer science and information retrieval.
"""
print("Adding text to cognee:")
print(text.strip())
# Add the text, and make it available for cognify
await cognee.add(text)
# Use LLMs and cognee to create knowledge graph
await cognee.cognify()
print("Cognify process complete.\n")
query_text = "Tell me about NLP"
print(f"Searching cognee for insights with query: '{query_text}'")
# Query cognee for insights on the added text
search_results = await cognee.search(
query_text=query_text, query_type=SearchType.INSIGHTS
)
print("Search results:")
# Display results
for result_text in search_results:
print(result_text)
# Example output:
# ({'id': UUID('bc338a39-64d6-549a-acec-da60846dd90d'), 'updated_at': datetime.datetime(2024, 11, 21, 12, 23, 1, 211808, tzinfo=datetime.timezone.utc), 'name': 'natural language processing', 'description': 'An interdisciplinary subfield of computer science and information retrieval.'}, {'relationship_name': 'is_a_subfield_of', 'source_node_id': UUID('bc338a39-64d6-549a-acec-da60846dd90d'), 'target_node_id': UUID('6218dbab-eb6a-5759-a864-b3419755ffe0'), 'updated_at': datetime.datetime(2024, 11, 21, 12, 23, 15, 473137, tzinfo=datetime.timezone.utc)}, {'id': UUID('6218dbab-eb6a-5759-a864-b3419755ffe0'), 'updated_at': datetime.datetime(2024, 11, 21, 12, 23, 1, 211808, tzinfo=datetime.timezone.utc), 'name': 'computer science', 'description': 'The study of computation and information processing.'})
# (...)
#
# It represents nodes and relationships in the knowledge graph:
# - The first element is the source node (e.g., 'natural language processing').
# - The second element is the relationship between nodes (e.g., 'is_a_subfield_of').
# - The third element is the target node (e.g., 'computer science').
if __name__ == '__main__':
asyncio.run(main())
For more advanced usage, have a look at our documentation.
Understand our architecture

Demos
What is AI memory:
Code of Conduct
We are committed to making open source an enjoyable and respectful experience for our community. See CODE_OF_CONDUCT for more information.




