## Description This PR adds usage frequency tracking to help identify which graph elements (nodes) are most frequently accessed during user searches. **Related Issue:** Closes [#1458] **The Problem:** When users search repeatedly, we had no way to track which pieces of information were being referenced most often. This made it impossible to: - Prioritize popular content in search results - Understand which topics users care about most - Improve retrieval by boosting frequently-used nodes **The Solution:** I've implemented a system that tracks usage patterns by: 1. Leveraging the existing `save_interaction=True` flag in `cognee.search()` which creates `CogneeUserInteraction` nodes 2. Following the `used_graph_element_to_answer` edges to see which graph elements each search referenced 3. Counting how many times each element was accessed within a configurable time window (default: 7 days) 4. Writing a `frequency_weight` property back to frequently-accessed nodes This gives us a simple numeric weight on nodes that reflects real usage patterns, which can be used to improve search ranking, analytics dashboards, or identifying trending topics. **Key Design Decisions:** - Time-windowed counting (not cumulative) - focuses on recent usage patterns - Configurable minimum threshold - filters out noise from rarely accessed nodes - Neo4j-first implementation using Cypher queries - works with our primary production database - Documented Kuzu limitation - requires schema changes, leaving for future work as acceptable per team discussion The implementation follows existing patterns in Cognee's memify pipeline and can be run as a scheduled task or on-demand. **Known Limitations:** **Kuzu adapter not currently supported** - Kuzu requires properties to be defined in the schema at node creation time, so dynamic property updates don't work. I'm opening a separate issue to track Kuzu support, which will require schema modifications in the Kuzu adapter. For now, this feature works with Neo4j (our primary production database). **Follow-up Issue:** #1993 ## Acceptance Criteria **Core Functionality:** - ✅ `extract_usage_frequency()` correctly counts node access frequencies from interaction data - ✅ `add_frequency_weights()` writes `frequency_weight` property to Neo4j nodes - ✅ Time window filtering works (only counts recent interactions) - ✅ Minimum threshold filtering works (excludes rarely-used nodes) - ✅ Element type distribution tracked for analytics - ✅ Gracefully handles unsupported adapters (logs warning, doesn't crash) **Testing Verification:** 1. Run the end-to-end example with Neo4j: ```bash # Update .env for Neo4j GRAPH_DATABASE_PROVIDER=neo4j GRAPH_DATASET_HANDLER=neo4j_aura_dev python extract_usage_frequency_examplepy ``` Should show frequencies extracted and applied to nodes 2. Verify in Neo4j Browser (http://localhost:7474): ```cypher MATCH (n) WHERE n.frequency_weight IS NOT NULL RETURN n.frequency_weight, labels(n), n.text ORDER BY n.frequency_weight DESC LIMIT 10 ``` Should return nodes with frequency weights 3. Run unit tests: ```bash python test_usage_frequency.py ``` All tests pass (tests are adapter-agnostic and test core logic) 4. Test graceful handling with unsupported adapter: ```bash # Update .env for Kuzu GRAPH_DATABASE_PROVIDER=kuzu GRAPH_DATASET_HANDLER=kuzu python extract_usage_frequency_example.py ``` Should log warning about Kuzu not being supported but not crash **Files Added:** - `cognee/tasks/memify/extract_usage_frequency.py` - Core implementation (215 lines) - `extract_usage_frequency_example.py` - Complete working example with documentation - `test_usage_frequency.py` - Unit tests for core logic - Test utilities and Neo4j setup scripts for local development **Tested With:** - Neo4j 5.x (primary target, fully working) - Kuzu (gracefully skips with warning) - Python 3.10, 3.11 - Existing Cognee interaction tracking (save_interaction=True) **What This Solves:** This directly addresses the need for usage-based ranking mentioned in [#1458]. Now teams can: - See which information gets referenced most in their knowledge base - Build analytics dashboards showing popular topics - Weight search results by actual usage patterns - Identify content that needs improvement (low frequency despite high relevance) ## Type of Change - [x] New feature (non-breaking change that adds functionality) ## Screenshots **Output from running the E2E example showing frequency extraction:** <img width="1125" height="664" alt="image" src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/455c1ee4-525d-498b-8219-8f12a15292eb" /> <img width="1125" height="664" alt="image" src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/64d5da31-85db-427b-b4b4-df47a9c12d6f" /> <img width="822" height="456" alt="image" src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/69967354-d550-4818-9aff-a2273e48c5f3" /> **Neo4j Browser verification:** ``` ✓ Found 6 nodes with frequency_weight in Neo4j! Sample weighted nodes: - Weight: 37, Type: ['DocumentChunk'] - Weight: 30, Type: ['Entity'] ``` ## Pre-submission Checklist - [x] **I have tested my changes thoroughly before submitting this PR** - [x] **This PR contains minimal changes necessary to address the issue/feature** - [x] My code follows the project's coding standards and style guidelines - [x] I have added tests that prove my fix is effective or that my feature works - [x] I have added necessary documentation (if applicable) - [x] All new and existing tests pass - [x] I have searched existing PRs to ensure this change hasn't been submitted already - [x] I have linked any relevant issues in the description - [x] My commits have clear and descriptive messages ## DCO Affirmation I affirm that all code in every commit of this pull request conforms to the terms of the Topoteretes Developer Certificate of Origin. <!-- This is an auto-generated comment: release notes by coderabbit.ai --> ## Summary by CodeRabbit ## Release Notes * **New Features** * Added usage frequency extraction that aggregates interaction data and weights frequently accessed graph elements. * Frequency analysis supports configurable time windows, minimum interaction thresholds, and element type filtering. * Automatic frequency weight propagation to Neo4j, Kuzu, and generic graph database backends. * **Documentation** * Added comprehensive example script demonstrating end-to-end usage frequency extraction, weighting, and analysis. <sub>✏️ Tip: You can customize this high-level summary in your review settings.</sub> <!-- end of auto-generated comment: release notes by coderabbit.ai --> |
||
|---|---|---|
| .github | ||
| alembic | ||
| assets | ||
| bin | ||
| cognee | ||
| cognee-frontend | ||
| cognee-mcp | ||
| cognee-starter-kit | ||
| deployment | ||
| distributed | ||
| evals | ||
| examples | ||
| licenses | ||
| logs | ||
| new-examples | ||
| notebooks | ||
| tools | ||
| working_dir_error_replication | ||
| .coderabbit.yaml | ||
| .dockerignore | ||
| .env.example | ||
| .env.template | ||
| .gitattributes | ||
| .gitguardian.yml | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| .mergify.yml | ||
| .pre-commit-config.yaml | ||
| .pylintrc | ||
| AGENTS.md | ||
| alembic.ini | ||
| CLAUDE.md | ||
| CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md | ||
| CONTRIBUTING.md | ||
| CONTRIBUTORS.md | ||
| DCO.md | ||
| docker-compose.yml | ||
| Dockerfile | ||
| entrypoint.sh | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| mise.toml | ||
| mypy.ini | ||
| NOTICE.md | ||
| poetry.lock | ||
| pyproject.toml | ||
| README.md | ||
| SECURITY.md | ||
| uv.lock | ||

Cognee - Accurate and Persistent AI Memory
Demo . Docs . Learn More · Join Discord · Join r/AIMemory . Community Plugins & Add-ons
Use your data to build personalized and dynamic memory for AI Agents. Cognee lets you replace RAG with scalable and modular ECL (Extract, Cognify, Load) pipelines.
🌐 Available Languages : Deutsch | Español | Français | 日本語 | 한국어 | Português | Русский | 中文
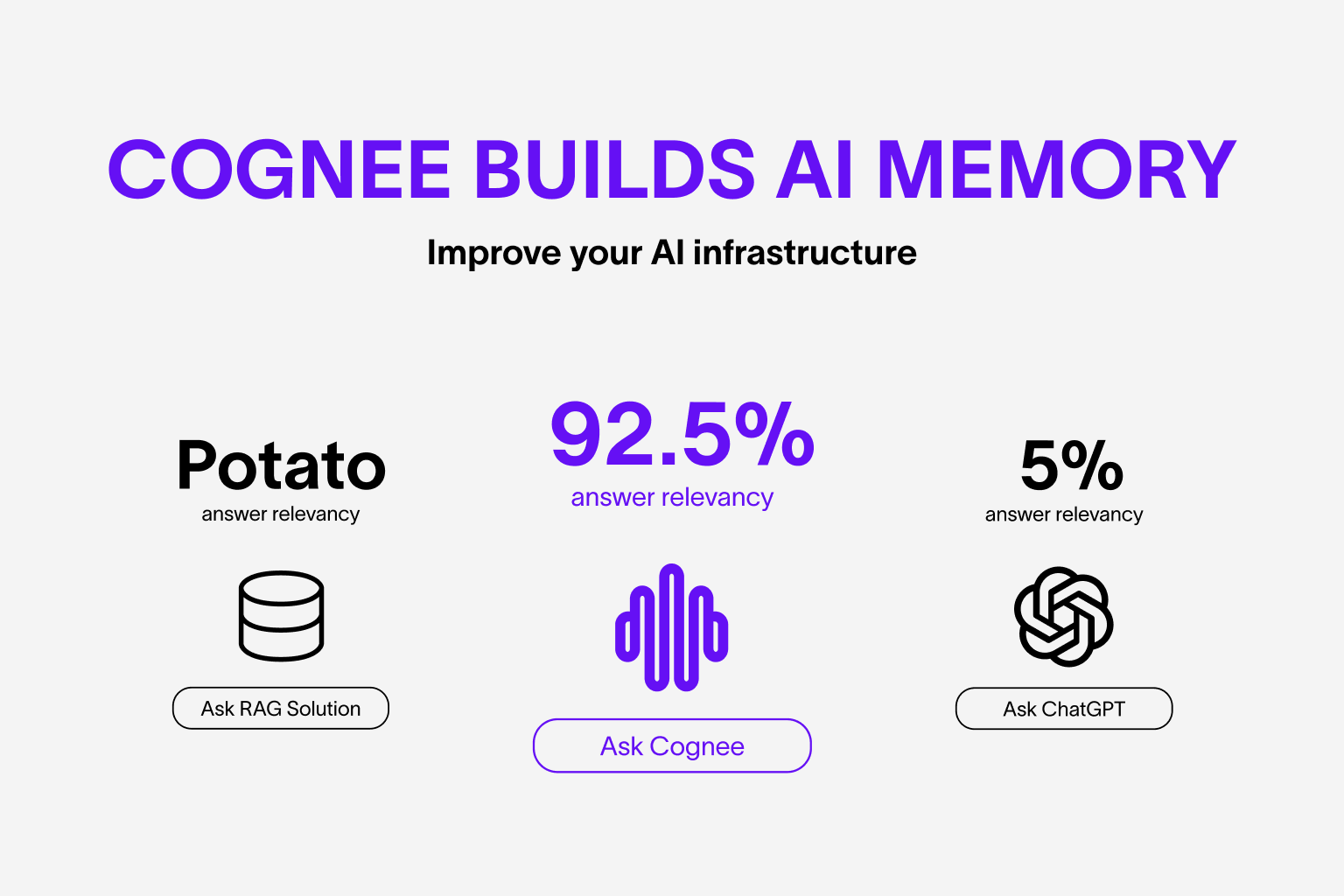
About Cognee
Cognee is an open-source tool and platform that transforms your raw data into persistent and dynamic AI memory for Agents. It combines vector search with graph databases to make your documents both searchable by meaning and connected by relationships.
You can use Cognee in two ways:
- Self-host Cognee Open Source, which stores all data locally by default.
- Connect to Cognee Cloud, and get the same OSS stack on managed infrastructure for easier development and productionization.
Cognee Open Source (self-hosted):
- Interconnects any type of data — including past conversations, files, images, and audio transcriptions
- Replaces traditional RAG systems with a unified memory layer built on graphs and vectors
- Reduces developer effort and infrastructure cost while improving quality and precision
- Provides Pythonic data pipelines for ingestion from 30+ data sources
- Offers high customizability through user-defined tasks, modular pipelines, and built-in search endpoints
Cognee Cloud (managed):
- Hosted web UI dashboard
- Automatic version updates
- Resource usage analytics
- GDPR compliant, enterprise-grade security
Basic Usage & Feature Guide
To learn more, check out this short, end-to-end Colab walkthrough of Cognee's core features.
Quickstart
Let’s try Cognee in just a few lines of code. For detailed setup and configuration, see the Cognee Docs.
Prerequisites
- Python 3.10 to 3.13
Step 1: Install Cognee
You can install Cognee with pip, poetry, uv, or your preferred Python package manager.
uv pip install cognee
Step 2: Configure the LLM
import os
os.environ["LLM_API_KEY"] = "YOUR OPENAI_API_KEY"
Alternatively, create a .env file using our template.
To integrate other LLM providers, see our LLM Provider Documentation.
Step 3: Run the Pipeline
Cognee will take your documents, generate a knowledge graph from them and then query the graph based on combined relationships.
Now, run a minimal pipeline:
import cognee
import asyncio
async def main():
# Add text to cognee
await cognee.add("Cognee turns documents into AI memory.")
# Generate the knowledge graph
await cognee.cognify()
# Add memory algorithms to the graph
await cognee.memify()
# Query the knowledge graph
results = await cognee.search("What does Cognee do?")
# Display the results
for result in results:
print(result)
if __name__ == '__main__':
asyncio.run(main())
As you can see, the output is generated from the document we previously stored in Cognee:
Cognee turns documents into AI memory.
Use the Cognee CLI
As an alternative, you can get started with these essential commands:
cognee-cli add "Cognee turns documents into AI memory."
cognee-cli cognify
cognee-cli search "What does Cognee do?"
cognee-cli delete --all
To open the local UI, run:
cognee-cli -ui
Demos & Examples
See Cognee in action:
Persistent Agent Memory
Cognee Memory for LangGraph Agents
Simple GraphRAG
Cognee with Ollama
Community & Support
Contributing
We welcome contributions from the community! Your input helps make Cognee better for everyone. See CONTRIBUTING.md to get started.
Code of Conduct
We're committed to fostering an inclusive and respectful community. Read our Code of Conduct for guidelines.
Research & Citation
We recently published a research paper on optimizing knowledge graphs for LLM reasoning:
@misc{markovic2025optimizinginterfaceknowledgegraphs,
title={Optimizing the Interface Between Knowledge Graphs and LLMs for Complex Reasoning},
author={Vasilije Markovic and Lazar Obradovic and Laszlo Hajdu and Jovan Pavlovic},
year={2025},
eprint={2505.24478},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.AI},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.24478},
}





